Chat Components
Chat Components are used to create rich text messages in Minecraft. They can include formatting, interactivity, and nested components. Kore has functions to create and manipulate Chat Components in a datapack.
Note that they always works by groups named ChatComponents, whenever you create a chat component, you actually create a ChatComponents, and you can chain multiple components together using the + operator.
Minecraft sometimes does not allow "complex" chat components with data resolving (score, nbt and entity chat components), if you use them, you'll get an empty text component. Simple chat components are inheriting the SimpleComponent interface, and you have a containsOnlySimpleComponents property to check if a ChatComponents only contains simple components.
You also have a containsOnlyText() function to check if a ChatComponents only contains plain text components with no formatting.
Common Properties
bold- Whether the text is bold.clickEvent- The action to perform when the text is clicked.color- The color of the text.extra- Additional components to display after this one (prefer using the+operator).font- The font to use.hoverEvent- The action to perform when the text is hovered over.insertion- The text to insert into the chat when the text is shift-clicked.italic- Whether the text is italic.obfuscated- Whether the text is obfuscated.strikethrough- Whether the text is strikethrough.text- The text to display.underlined- Whether the text is underlined.
PlainTextComponent
The PlainTextComponent displays simple text with optional formatting such as color and bold.
To create a PlainTextComponent, use the textComponent function.
Example
In-game output: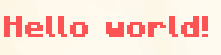
See how to set custom colors in the Colors article.
Combined Components
Components can be combined using the + operator, use the text function to create a simple text component and not a ChatComponents.
In-game output: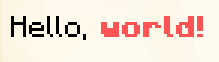
(only the "world!" part is bold and red)
EntityComponent
The EntityComponent displays the name of an entity selected by a selector. If multiple entities are found, their names are displayed in the form Name1, Name2 etc.
The separator property can be used to change the separator between the names of the entities.
If no entities are found, the component displays nothing.
Example
In-game example: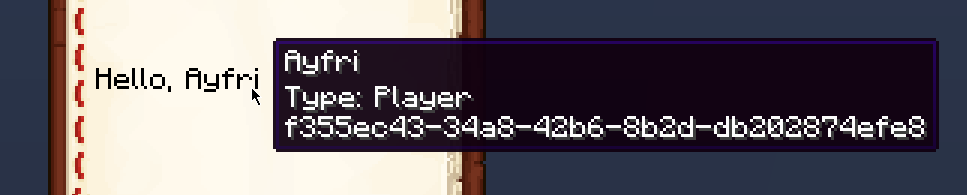
KeybindComponent
The KeybindComponent displays a keybind. The keybind is displayed in the player's keybind settings.
Example
In-game example: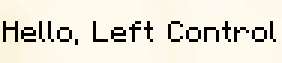
NbtComponent
The NbtComponent displays NBT data from a block, an entity, or a storage. The interpret property can be used to interpret the NBT data as a text component, if the parsing fails, nothing is displayed.
The nbt property can be used to specify the path to the NBT data.
If nbt points to an array, then it will display all the elements joined in the form Element1, Element2 etc.
The separator property can be used to change the separator between the elements of the array.
Example
In-game output: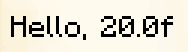
ScoreComponent
The ScoreComponent displays the score of an entity for a specific objective. The name property can be used to specify the name of the entity whose score to display, it can be a selector or a literal name (will use the player with that name). It can also be * to select the entity seeing the text component.
The objective property can be used to specify the name of the objective to display the score of.
A value property can be used to specify a fixed value to display regardless of the score.
Example
In-game output: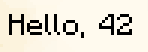
TranslatedTextComponent
The TranslatedTextComponent displays translated text using translation keys. You can also pass arguments to the translation key with the with argument, which should be a list of text components or strings.
A fallback property can be used to specify a fallback text if the translation key is not found.
Example
In-game output: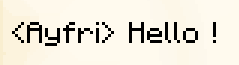
Hover Event
Hover events display extra information when the text is hovered over, it can be either text, an item, or an entity. Use showText to display text, showItem to display an item, and showEntity to display an entity.
Note that to show an entity, you have to have its UUID as a string.
Hover Event Example
In-game output:
Hover Item Example
In-game output: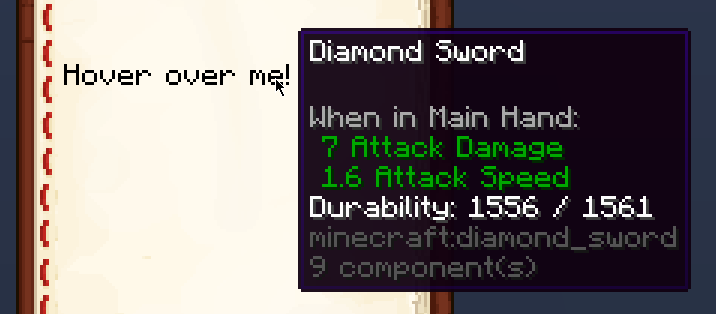
Click Event
Click events perform an action when the text is clicked. The action can be to:
- Change the page of the book if reading a book
- Copy some text to the clipboard
- Open a file
- Open a URL
- Run a command
- Suggest a command (insert the command in the chat but don't run it)
Click Event Example
Object Components
Object components render atlas sprites or player skins inside chat. They require the ObjectTextComponent family and can be built via objectComponent or playerObjectComponent depending on the source.
AtlasObjectTextComponent
atlas - The atlas that contains the sprite. Optional when the sprite already resolves to an atlas entry, otherwise provide an explicit AtlasArgument.
sprite- TheModelArgumentthat identifies the sprite to render and is required.
Use objectComponent to construct atlas objects, optionally passing an atlas override.
In-game output:
PlayerObjectTextComponent
hat- Whether to display the player's hat layer (true/false) or leave it untouched when null.player- APlayerProfiledescribing the skin whose head should render; provide either a name, UUID, or both plus properties.
playerObjectComponent accepts a PlayerProfile, name, or UUIDArgument, and the nested player block lets you add PlayerProperty estimations.
In-game output:
Notice that there is a shadow on the player's head, you can disable it by setting shadowColor to 0.
In-game output:
These components respect the same formatting as any other chat component, so you can still chain them, color them, or attach hover and click behaviors.
